Introduction to Quinoa
Quinoa, scientifically known as Chenopodium quinoa , is a pseudocereal that has gained popularity around the world in the last decade. This seed, which has been cultivated for thousands of years in the Andean region, has been a staple food for many pre-Columbian civilizations and remains a vital component in the modern diet of many Peruvians.
Origin and history of quinoa in Peru
The history of quinoa in Peru dates back more than 5000 years. The ancient civilizations that inhabited the Andean region, such as the Incas, considered quinoa a sacred grain and called it “the mother of all grains.” This veneration was not unfounded; Quinoa played an essential role in their diet, offering sustenance and nutrition in the high altitudes of the Andes.
The cultivation and consumption of quinoa in Peruvian territory was not only limited to the Incas. Before their rule, various pre-Inca cultures had already incorporated this grain into their daily diet. With the arrival of the Spanish to the American continent in the 16th century, quinoa, along with other native crops, suffered a period of decline due to the prohibitions and agricultural policies of the colonizers, who prioritized European crops.
However, despite these challenges, quinoa persisted in the rural regions of the Andes, where local communities continued to cultivate it and pass on their techniques and knowledge from generation to generation. It was not until recent decades that quinoa began to be recognized internationally for its nutritional qualities and its adaptability to different climatic conditions, becoming a valuable export crop for countries like Peru.
Nutritional value and health benefits
Quinoa is more than just a food; It is a rich and diverse source of essential nutrients. It is one of the few vegetables that contains all nine essential amino acids, meaning it is a complete protein, ideal for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
In addition to being rich in protein, quinoa is an excellent source of fiber, which aids in digestion and may help reduce the risk of heart disease. It is also rich in minerals such as magnesium, iron, phosphorus and zinc. Its low glycemic index makes it suitable for diabetics and people looking to regulate their blood sugar level.
One of the most notable benefits of quinoa is its antioxidant content, which can help fight free radicals in the body and prevent chronic diseases. Also, because it is naturally gluten-free, it has become a popular choice for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Incorporating quinoa into your diet is not only nutritionally beneficial, but also offers culinary versatility. It can be cooked and consumed in various ways, from salads and stews to desserts and drinks.
Quinoa production in Peru
Peru, the birthplace of quinoa, is one of the main producers and exporters of this pseudocereal in the world. The country’s geographical richness, which ranges from coastal valleys to high Andean mountains, allows it to grow various varieties of quinoa, each with unique characteristics. But beyond its geographical versatility, it is the cultural heritage and ancestral agricultural techniques that have allowed Peru to stand out in the production of quality quinoa.
Main growing regions
Quinoa is grown in various regions of Peru, from the coast to the mountains, each one providing different characteristics to the grain depending on its climate and soil.
- Puno: It is the main quinoa producing department in the country. Located on the high plateau, on the shores of Lake Titicaca, this place offers ideal conditions for high-quality varieties of quinoa.
- Cusco: Another outstanding Andean region, which produces quinoa mainly in its provinces of Urubamba and Calca.
- Arequipa: In the highest areas of this region, especially in the province of Caylloma, quinoa finds a favorable habitat.
- Ayacucho and Apurímac: These regions, located in the central Andes, also have significant production, providing diversity to the Peruvian quinoa landscape.
Agricultural techniques and practices
The cultivation of quinoa in Peru is a mix of traditional techniques, transmitted from generation to generation, and modern agricultural practices that seek to optimize production.
- Crop rotation: An ancient practice that maintains soil fertility and prevents the proliferation of pests and diseases.
- Organic agriculture: Many quinoa producers opt for organic techniques, avoiding the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers, which has allowed them to access demanding international markets.
- Minimum tillage: This technique preserves soil structure and reduces erosion, crucial in mountainous areas.
- Use of bioinputs: The application of beneficial microorganisms and other natural inputs reinforces the health of the plant and the soil.
Featured Peruvian varieties
Peru is home to an impressive diversity of quinoa varieties, many of which are endemic to the region.
- White quinoa: Originally from Puno and highly appreciated for its mild flavor and delicate texture.
- Red quinoa: With a firmer grain and a slightly earthier flavor, it is ideal for salads and cold dishes.
- Black quinoa: It is rich in antioxidants and has a more intense flavor, perfect for robust dishes.
- Tricolor Quinoa: A visually attractive and nutritious mix that combines white, red and black varieties.
These varieties, along with other less known but equally valuable varieties, make Peruvian quinoa a nutritional treasure that the world has begun to discover and value.
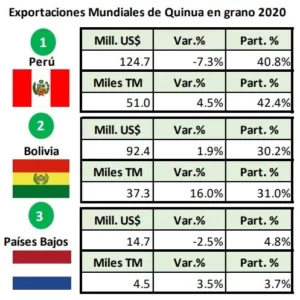
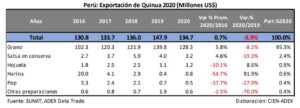
Peruvian quinoa export history
The global recognition of quinoa as a “super food” has been a blessing for Peru, a country that has cultivated and valued this pseudocereal since pre-Hispanic times. Quinoa exports have seen an upward trend in recent decades, with trade flows reflecting not only the quality of the Peruvian grain, but also the country’s ability to adapt to the demands of a constantly evolving global market.
Evolution over the years
Peruvian quinoa exports have taken a fascinating path, which can be summarized in several key stages:
- 1980s-1990s: During this period, quinoa was primarily a local crop with little international recognition. Exports were minimal and aimed mainly at specific niches.
- 2000s: With the growth of interest in healthy and organic foods, international demand for quinoa began to increase. Starting in the 2000s, Peruvian quinoa exports began to grow steadily.
- Year 2013: The United Nations General Assembly declared 2013 as the “International Year of Quinoa”, with Peru and Bolivia leading the way in promoting the grain. This gave a strong boost to the global visibility and demand for quinoa.
- Years 2010-2020: During this decade, Peruvian exports of quinoa reached record figures, positioning Peru as one of the main world exporters. Despite some fluctuations, such as the decline in 2023, the overall trend has been positive.
Comparison with other exporting countries
Globally, there are several key players in the quinoa export market:
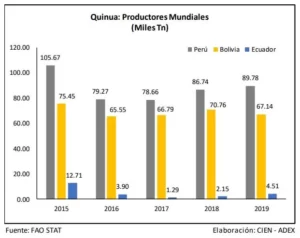
- Bolivia: Traditionally it has been Peru’s main competitor in the quinoa market. Like Peru, Bolivia has a rich diversity of quinoa and a long history of cultivation.
- Ecuador: Although its production is lower compared to Peru and Bolivia, Ecuador has been increasing its presence in the global market.
- United States and Canada: Although they are net consumers of quinoa, in recent years, they have begun to grow it locally, reducing dependence on imports.
In comparison, although other countries have increased their production and exports, Peruvian quinoa is distinguished by its quality, diversity and international recognition. Even so, the dynamism of the market requires that Peru continue to innovate and ensure excellence in its production and export chain.
Importance of the US market
The US market has established itself as the main destination for Peruvian quinoa exports. This predilection is no coincidence, since the United States has experienced a boom in the consumption of healthy foods and quinoa has positioned itself as one of the favorites in this segment. This trade relationship represents a golden opportunity for Peru, but it is also accompanied by certain challenges.
Consumption growth in the US
The last decade has seen America’s explosive interest in quinoa. Some factors that have driven this growth are:
- Food trends: With the increase in vegetarian, vegan and other specialized diets, quinoa has become popular as a complete source of protein.
- Health promotion: Awareness campaigns about the benefits of quinoa, rich in fiber, minerals and essential amino acids, have influenced its consumption.
- Diversified cuisine: Globalization and interest in international cuisines have led chefs and households to experiment with foreign ingredients, and quinoa has been one of the main beneficiaries.
- International recognition: Events such as the “International Year of Quinoa” in 2013 have also had an impact on the perception and consumption of the grain in the US.
Advantages and challenges of the North American market
Advantages :
- High purchasing power: American consumers have significant purchasing power, which can translate into premium prices for high-quality products like Peruvian quinoa.
- Consumer Diversity: The vast and diverse US market allows marketing efforts to be segmented and focused on specific niches, from fitness enthusiasts to gourmets.
- Trade stability: With trade agreements and a history of bilateral relations, trade between Peru and the US has enjoyed stability and predictability.
Challenges :
- Rules and Regulations: The US market has strict health and quality regulations that can represent a challenge for some exporters.
- Local and international competition: The growing local production of quinoa in the United States and imports from other countries can saturate the market and put pressure on prices.
- Demand volatility: While quinoa is popular now, food trends change, and Peru must be prepared to adapt to market developments.
Other key international markets
Although the United States leads the list of importers of Peruvian quinoa, it is not the only market that demands this superfood. Canada and several European countries have shown sustained growth in their consumption. In addition, there are emerging markets that show promising potential, offering Peruvian exporters multiple opportunities to diversify their destinations.
Canada and Europe: demand and opportunities
Canada :
- Health Consciousness: Just like in the US, health and wellness are prevalent trends in Canada. Quinoa, with its impressive nutritional profile, has positioned itself as an essential food for many Canadians.
- Cultural diversity: Canada’s rich cultural diversity, with a significant immigrant population, has led to an openness to international foods, including quinoa.
- Trade relations: The existing trade agreements between Peru and Canada facilitate exports and promote commercial exchange.
Europe :
- Food trends: Countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Italy and the Netherlands have shown an increase in demand for organic and healthy foods, where quinoa has firmly established itself.
- Favorable regulations: The European Union has regulations that favor the import of organic and sustainable products, which benefits Peruvian quinoa grown under these standards.
- Promotion and distribution: Various food festivals and trade fairs in Europe serve as platforms to present and promote Peruvian quinoa.
Emerging and potential markets
- Asia: Countries such as China, Japan and South Korea show growing interest in superfoods. Quinoa, still relatively new to these markets, has great potential, especially among the urban and healthy classes.
- Middle East: Countries such as the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia are diversifying their diets, opening up opportunities for quinoa as an alternative to traditional grains.
- Africa: Although the continent is still in the early stages of adopting quinoa, countries such as South Africa and Nigeria are showing interest due to its nutritional profile and quinoa’s ability to grow in adverse conditions.
Exploring and adapting to these emerging markets can be key to ensuring the future of Peruvian quinoa exports on the global stage.
The global competition
Quinoa, native to the Andean region, has taken the global stage by storm. Its fame as a superfood has encouraged many countries to begin its cultivation, leading to growing competition in the international market. Although Peru has traditionally been one of the largest exporters, it faces increasing competition, leading it to seek innovative strategies to maintain its position.
New competitors on the scene
- Bolivia: Although it is not a “new” competitor, Bolivia has been a traditional exporter along with Peru. With exclusive varieties of quinoa and a strong tradition in its cultivation, Bolivia has intensified its efforts to position itself in the global market.
- Ecuador: With geographical conditions similar to those of Peru, Ecuador has increased its production and export of quinoa in recent years, seeking a piece of the international market.
- India and Nepal: These countries have started experimenting with growing quinoa due to its adaptability to different climatic conditions. Although they are in the early stages, they represent potential competitors in the future.
- United States and Canada: These northern countries have begun growing quinoa on a small scale to meet local demand, thus reducing dependence on imports.
Competition and differentiation strategies
- Certifications: Obtaining certifications such as “organic”, “fair trade” or “non-GMO” (without genetically modified organisms) can increase demand and differentiate Peruvian quinoa in international markets.
- Exclusive varieties: Promoting unique varieties of quinoa that are only found in Peru can be an effective strategy to distinguish yourself from other competitors.
- History and culture: The rich history of quinoa in Andean culture can be a valuable marketing tool. Telling the story of how quinoa has been part of the Andean diet for thousands of years can capture the imagination of consumers.
- Product innovation: In addition to selling quinoa in its raw form, Peruvian exporters can explore the creation of derived products such as snacks, drinks, pasta, among others.
- Trade relations and agreements: Strengthening and establishing new trade agreements with importing countries can facilitate entry and consolidation in those markets.
In this competitive landscape, it is essential that Peru continues to innovate and strengthen its image as a leader in the production and export of high-quality quinoa.
Leading export companies
The Peruvian quinoa market has been dominated by several companies that, through their commercial practices and marketing strategies, have managed to establish themselves as leaders on the international stage. These companies have played a crucial role in bringing Peruvian quinoa to tables around the world.
Alisur SA and its dominance in the market
- History and Origins: Alisur SA has established itself as one of the main quinoa exporting companies in Peru. Founded in [Foundation Date – specific research required], it has grown steadily thanks to its sustainable practices and commitment to quality.
- Infrastructure and Capacity: With modern facilities and advanced technology, Alisur SA guarantees a top quality product that meets the most demanding international standards.
- Commercial Strategies: Alisur SA has established strong relationships with distributors in the main markets, which allows them to have a global reach. In addition, they have invested in marketing and promotion to consolidate the brand and generate recognition.
- Commitment to the Community: One of Alisur SA’s strengths is its commitment to local farming communities. Through partnerships and support programs, they ensure sustainable agricultural practices and improve the living conditions of the farmers with whom they work.
Other notable Peruvian exporters
- Olam Global Agri Perú SAC: With significant sales, this company has positioned itself as one of the leaders in the export of quinoa. Its focus on sustainable practices and quality has been key to its success in international markets.
- Colorexa SAC: This company has demonstrated an exceptional ability to adapt to changing market demands, which has allowed it to remain a key player in the industry.
- Wiraccocha del Perú SAC: With a strong tradition and knowledge in the cultivation of quinoa, they have managed to establish themselves in foreign markets thanks to their commitment to excellence.
- Agrofino Foods SAC and Xpodeka SAC: These companies, although with smaller amounts compared to Alisur SA, have managed to stand out thanks to their innovative strategies and solid commercial relationships.
The consolidation of these companies in the international market demonstrates the potential and quality of Peruvian quinoa. Its success not only boosts the national economy, but also reinforces Peru’s position as a world leader in quinoa exports.
Logistical challenges and problems
The export of quinoa from Peru, despite its success and growth in international markets, is not without challenges. Logistical obstacles can represent significant limitations for exporters, affecting both the efficiency and profitability of their operations.
Limitations in the supply chain
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Although Peru has made progress in improving its infrastructure, there are still production areas where access is limited, complicating the transportation of quinoa from the field to the processing centers.
- Storage Challenges: Quinoa requires specific storage conditions to maintain its quality. Lack of adequate facilities can lead to post-harvest losses.
- Transportation Time and Cost: Given the long distances and transit times to certain key markets, it is essential that quinoa is transported in optimal conditions to ensure it arrives fresh and in good condition.
- Bureaucracy and Procedures: Exporting requires a series of procedures and documentation that, if not handled properly, can result in delays and additional costs.
Challenges in production and quality
- Climate Variability: Unexpected changes in climate can affect the quinoa harvest, leading to lower yields and challenges in maintaining consistent quality.
- Agricultural Practices: Despite the tradition in quinoa cultivation, there are still areas where better agricultural practices are needed to ensure high quality harvests year after year.
- Pests and Diseases: Quinoa, like any other crop, is susceptible to various pests and diseases that can affect its yield and quality.
- International Standards: Each destination market has its own quality standards and regulations. Staying up to date and meeting these standards can be a constant challenge for producers.
These challenges, while significant, also present opportunities. Those companies and producers that can overcome these obstacles will be in a strong position to take advantage of the growing opportunities in the global quinoa market.
Branding and marketing strategies
Peruvian quinoa is not simply an agricultural product: it is a brand with history, culture and unique characteristics. To stand out in the international market, it is essential that Peruvian companies develop effective branding and marketing strategies that highlight their competitive advantages.
Product differentiation: Designation of origin
- History and Culture: Quinoa has been cultivated in the Andean region for thousands of years, and its history can be a powerful marketing tool. Relating quinoa to the ancient Incas, for example, can evoke images of an ancient and authentic food.
- Certification of Origin: A protected “Denomination of Origin” can be an effective way to ensure that only genuinely Peruvian quinoa can be sold as such. This can help ensure the quality and authenticity of the product in the international market.
- Distinctive Quality: Peruvian quinoa has unique characteristics in terms of flavor, texture and color. These differences must be clearly communicated to consumers so that they value and seek out quinoa originating from Peru over other variants.
Digital marketing and promotion strategies
- Online Presence: Having a well-designed website that tells the story of Peruvian quinoa, offers recipes, and provides information about its health benefits can be an essential tool in the digital age.
- Social Networks: Platforms such as Instagram, Facebook and Pinterest are ideal for promoting food, as they allow you to share appetizing images and innovative recipes that use quinoa.
- Collaborations with Influencers: Working with food bloggers, chefs, and other food influencers can help introduce Peruvian quinoa to a broader audience.
- Targeted Advertising: Using digital advertising tools to reach specific market segments, such as people interested in healthy foods or vegetarian cuisine, can be highly effective.
- Promotions and Discounts: Special offers, discounts and promotions can encourage consumers to try Peruvian quinoa, especially if they have never tried it before.
With well-executed branding and marketing strategies, Peruvian quinoa can strengthen its position in the global market, standing out not only for its quality but also for its rich history and culture.
Product innovation and diversification
Quinoa, due to its versatility and nutritional benefits, presents vast potential for innovation and diversification. While the grain itself is very popular, there are many ways in which it can be transformed and improved to suit new markets and changing tastes.
Development of derivative products
- Processed Quinoa: As demand for convenient foods grows, processed quinoa such as breakfast cereals, energy bars and quinoa-based pastas can offer faster and easier options for consumers.
- Drinks: Quinoa-based drinks, such as plant-based milks or smoothies, can be a great way to take advantage of the ever-expanding healthy drink market.
- Quinoa Flour: Used for baked goods, cookies, tortillas and others, this flour is an excellent gluten-free and high-protein alternative to conventional flour.
- Snacks and Chips: Quinoa can also be used to produce snacks and chips, taking advantage of the healthy snack market.
Research and improved varieties
- Resistant Varieties: With the challenges of climate change and pests, it is crucial to research and develop quinoa varieties that are more resistant to these problems and can thrive in various conditions.
- Nutritional Improvement: Through research, quinoa varieties can be developed with an even more outstanding nutritional profile, for example, with more protein, fewer carbohydrates or more micronutrients.
- Adaptation to Different Soils: Given the diversity of climates and soils in the world, developing varieties that can grow in different types of soil can increase the reach of quinoa.
- Integration with Modern Agricultural Technologies: The adaptation of quinoa to modern agricultural technologies, such as precision agriculture, can improve yields and production efficiency.
Innovation and diversification can not only help Peruvian companies stay at the forefront of the global quinoa market, but also open new markets and opportunities. With the right investment in research and development, Peruvian quinoa has the potential to expand its presence and popularity around the world.
Future prospects and trends
As global demand for healthy and sustainable foods continues to grow, the quinoa market has a promising horizon. Peru, as one of the main producers and exporters, is in a privileged position to capitalize on these trends. Some of the projections and emerging opportunities in the quinoa sector are analyzed below.
Growth projections for the coming years
- Growing Demand: As more consumers around the world recognize the health benefits of quinoa, demand is expected to continue to increase, especially in regions where knowledge of the grain is still emerging.
- Expansion in production: Given favorable climatic conditions and agricultural experience, Peru has the potential to further expand its quinoa production to meet growing global demand.
- Export Increase: As trade relationships are established and strengthened, Peruvian quinoa exports could see a significant increase in volume and value in the coming years.
- Sustainable development: With the rise of global interest in sustainable production, quinoa can play a key role as a resilient crop with low environmental impact.
New opportunities and markets
- Asia and the Middle East: These regions present emerging opportunities for quinoa due to a growing middle class and increased health awareness.
- Innovative products: As consumers seek variety, quinoa-derived products, such as beverages, snacks and supplements, can open new market opportunities.
- Organic Agriculture: The organic food market continues to grow globally. Producing certified organic quinoa could be a lucrative avenue for Peruvian producers.
- Partnerships and collaborations: Establishing alliances with international companies can help boost the Peruvian quinoa brand and access new markets easily.
The outlook for Peruvian quinoa is generally positive, and with the right strategy and planning, Peru could further consolidate its position as a global leader in the production and export of this superfood.
Socioeconomic impact in Peru
The rise of quinoa in international markets has had a multiplier effect in Peru, impacting not only the economy, but also the social fabric, particularly in rural areas. Being one of the main producers and exporters of quinoa in the world, the socioeconomic benefits and challenges in Peru are palpable.
Employment generation and rural development
- Agricultural employment: International demand for quinoa has led to an increase in labor hiring in rural areas, providing employment to thousands of farmers who previously relied on less profitable crops.
- Infrastructure development: Quinoa growing areas have seen improvements in local infrastructure, such as roads and irrigation systems, thanks to investments made to boost production.
- Education and training: Many farmers now have access to training programs that teach them modern agricultural techniques, increasing productivity and grain quality.
- Women Empowerment: In many regions, quinoa production has empowered women, offering them employment opportunities and leadership roles in cooperatives and agricultural organizations.
Economic benefits and social challenges
- Income and well-being: Quinoa has generated a significant source of income for Peruvian farmers, improving their quality of life and access to basic services.
- Marketing challenges: While quinoa has been profitable, it has also presented challenges in terms of marketing and competition, with farmers facing price fluctuations and global competition.
- Sustainability challenges: The boom can lead to overexploitation of land, which could affect soil quality and the long-term sustainability of production.
- Cultural change: Mass export has led to quinoa becoming more expensive for local consumption in some areas, which generates cultural and social tensions.
The socioeconomic impact of quinoa in Peru is complex and multifaceted. While it has brought many economic benefits, it has also presented challenges that require careful management to ensure sustainable and equitable development.
Legislation and regulations for exporters
The quinoa market, like any other product that seeks to establish itself in international markets, is not only governed by demand and supply, but also by a series of regulations, standards and standards that guarantee the quality, safety and sustainability of the product. Peruvian quinoa exporting companies, therefore, must be aware of these regulations, not only at the national but also international level.
National regulations and international agreements
- National regulations: In Peru, the Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation together with other State agencies establish regulations on the cultivation, processing and export of quinoa, ensuring that products meet certain standards.
- Free trade agreements: Peru has established trade agreements with several countries, which facilitates the export of quinoa to those markets under preferential terms.
- Tariff and non-tariff barriers: Despite the agreements, exporting companies must be informed about possible tariff or non-tariff barriers imposed by other countries.
- Phytosanitary agreements: These agreements refer to the rules established to prevent the introduction and spread of pests between countries, and are essential for the export of agricultural products such as quinoa.
Certifications and quality standards
- Organic certification: Given the global demand for organic foods, obtaining organic certification can open doors to more lucrative markets.
- Fair Trade Certification: This certification ensures that quinoa is produced under ethical and fair conditions, respecting the rights of farmers.
- ISO quality standards: These international standards guarantee that quinoa meets quality and safety standards for consumption.
- Denomination of origin: This seal protects the name of the quinoa produced in certain regions of Peru, guaranteeing its authenticity and quality.
Adhering to these regulations and standards not only ensures that Peruvian quinoa is accepted in international markets, but also increases consumer confidence in the quality and authenticity of the product.
Strategic alliances and partnerships
In a globalized world, strategic alliances and partnerships are crucial for any sector seeking to expand and strengthen in international markets. For the Peruvian quinoa market, these alliances have allowed us to share knowledge, technologies, open markets and, above all, strengthen the presence of the grain on the global table.
Collaborations with other countries and organizations
- Technological and knowledge exchange: Countries with strong agricultural traditions and advanced technologies can share their knowledge with Peru to improve the production and quality of quinoa.
- Joint research: Partnerships with universities and research centers in other countries can lead to research that addresses the challenges of quinoa cultivation and finds innovative solutions.
- Partnerships with NGOs and international organizations: These organizations often have programs that support sustainable development, organic agriculture and fair trade, and can be valuable allies for the Peruvian quinoa sector.
Free trade agreements and benefits
- Access to international markets: Free trade agreements (FTA) with countries and economic blocs allow Peru to export quinoa with preferential rates or even without tariffs, facilitating entry into those markets.
- Attracting investments: An FTA can encourage foreign investors to invest in the quinoa production chain in Peru, given the ease of later exporting the product.
- Establishing clear rules: These agreements also establish clear rules for trade and dispute resolution, creating a safer and more predictable business environment.
- Recognition and protection of the designation of origin: In some FTAs, clauses can be established that recognize and protect specific products from a country, such as quinoa from certain Peruvian regions.
Strategic alliances and trade agreements are essential for Peru to continue positioning its quinoa on the world stage and take full advantage of the opportunities that these agreements and associations offer.
Sustainability and responsible agricultural practices
Sustainability is a fundamental pillar in the current agricultural panorama. With growing global interest in responsible production and environmental care, quinoa farmers and producers in Peru face the challenge of balancing efficient production with sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
Environmental impact and conservation
- Efficient water use: Quinoa, native to arid regions, is a drought-tolerant plant. However, with demand increasing, it is crucial to efficiently manage water resources to ensure long-term sustainable production.
- Soil conservation: Crop rotation and other agricultural practices can prevent soil degradation and maintain soil fertility. Erosion is a problem in mountainous areas, so it is essential to apply techniques that prevent the loss of fertile land.
- Biodiversity: Preserving the genetic variety of quinoa is essential. Agricultural practices must guarantee the conservation of different varieties of quinoa, especially native ones.
- Reduction of emissions: The implementation of modern agricultural techniques can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the fight against climate change.
Organic agriculture and certifications
- Organic Quinoa: The demand for organic products has grown exponentially in recent years. The cultivation of organic quinoa, without the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers, can offer added value in the international market.
- Certifications: Certifications such as “USDA Organic”, “Fair Trade”, among others, are recognized worldwide and can open doors in markets where consumers value sustainable and ethical agricultural practices.
- Economic benefits: Organic and certified quinoa can often be sold at higher prices, benefiting farmers economically.
- Education and training: It is crucial that farmers receive training on how to obtain these certifications and on organic growing techniques.
Sustainability is not only essential from an environmental point of view, but can also be a competitive advantage in a global market increasingly aware of the importance of responsible production.
Training and training for producers
In a constantly evolving global market, training and training of producers is essential to maintain competitiveness and ensure sustainability. These programs not only improve the quality and quantity of production, but also ensure adaptability to new challenges and opportunities in the agricultural sector.
Training and education programs
- Support institutions: In Peru, various institutions, both governmental and non-governmental, offer training and education programs aimed at quinoa producers.
- Funding and Scholarships: Programs can be found that provide scholarships or funding for farmers who want to receive advanced training in agricultural techniques, agribusiness management, or even quinoa research.
- Technical training: These programs typically focus on teaching modern agricultural techniques, efficient water use, pest management, among other critical aspects of production.
- Digital tools: With the digitalization of the agricultural sector, some programs also train producers in the use of digital technologies and tools for crop management and monitoring.
Best practices and shared knowledge
- Cooperatives and associations: Agricultural cooperatives and producer associations are often valuable sources of shared knowledge. These organizations can facilitate the exchange of experiences and best practices between farmers.
- Events and fairs: Agricultural fairs, seminars and conferences provide opportunities for producers to update themselves on the latest trends, research and developments in the world of quinoa.
- Case studies: Analyzing and learning from successful producers or regions that have optimized their agricultural practices can be an effective way to adopt new strategies and techniques.
- Collaborative networks: Networking with experts, researchers and other producers can be an invaluable source of advice, solutions to common problems and new opportunities.
Continuous education and training is a key factor to ensure that quinoa producers in Peru are equipped with the necessary tools and knowledge to face the challenges of the future and take advantage of new opportunities.
Financing and economic support
Financing and economic support are fundamental pillars for the expansion and sustainability of the quinoa sector in Peru. Whether through government initiatives, agricultural banks, international organizations or private investors, these resources allow producers to innovate, expand and ultimately improve their profitability and competitiveness in the global market.
Credit programs and subsidies
- Agricultural loans: Banks and financial institutions in Peru offer specific loans for farmers, with favorable terms and competitive interest rates. These loans are usually used for the acquisition of machinery, seeds, or infrastructure improvements.
- Government subsidies: The Peruvian government, recognizing the importance of the agricultural sector, has established various subsidies that directly benefit quinoa producers. These may include subsidies for the purchase of inputs, the implementation of more sustainable technologies or the expansion of cultivation areas.
- Microfinance initiatives: In some regions, microfinance organizations provide support to small producers, offering them small-scale loans and financial training to effectively manage their businesses.
Investors and support for the sector
- Direct investment: Increasingly, national and international investors see Peruvian quinoa as an attractive business opportunity. Investment can be directed towards the creation of new farms, the expansion of existing ones or investment in innovative technologies and processes.
- Public-private partnerships: These partnerships typically emerge as collaborations between the government and private companies, and may include investments in research, infrastructure development, or training programs.
- International organizations: Organizations such as the World Bank or the FAO, among others, usually have programs to support the agricultural sector in developing countries, offering financing, training and technical advice.
The combination of adequate financing and economic support is essential to ensure that the quinoa industry in Peru continues to grow and prosper in the future, benefiting both producers and consumers globally.
Peruvian quinoa value chain
Understanding the Peruvian quinoa value chain is crucial to identifying the opportunities and challenges facing the sector. From its cultivation in the fields to its arrival on the consumer’s table, this product goes through a series of stages that involve various actors and processes. Analyzing this chain allows a holistic view of the business and can help improve the efficiency, quality and profitability of the final product.
From the field to the consumer
- Cultivation: It all begins with the selection of seeds and the preparation of the land. Here, the choice of varieties, agricultural techniques and management practices are essential to guarantee an abundant and quality harvest.
- Harvesting: Once the quinoa has reached its point of maturity, it is harvested. The technique and timing of harvesting are crucial to ensure that the grains retain all their properties.
- Primary processing: After harvesting, quinoa undergoes a cleaning, classification and drying process. These steps are essential to remove impurities and prepare the grain for storage or further processing.
- Storage: Proper conservation guarantees that quinoa maintains its quality and nutritional properties.
- Transformation: Depending on the final destination, quinoa can be processed into different forms: whole grains, flours, flakes, among others.
- Distribution and logistics: Once processed, the quinoa is packaged and distributed both in the domestic market and for export.
- Retail and consumption: Finally, it reaches stores, supermarkets and, eventually, the consumer’s home.
Roles y stakeholders clave
- Producers: They are the heart of the chain. Their work and decisions directly impact the quantity and quality of the quinoa produced.
- Input suppliers: Companies and individuals that provide seeds, fertilizers, machinery and other essential inputs for cultivation.
- Intermediaries: They often act as a link between the producer and the markets, facilitating the sale and distribution of the grain.
- Processors: Responsible for transforming quinoa into various products for consumption.
- Distributors and retailers: They play an essential role in bringing the product to the end consumer, whether in local or international markets.
- Regulatory and certifying entities: They establish and monitor compliance with quality and organic standards, among others.
- Consumers: Their demand and preferences guide many of the decisions in the value chain.
Understanding this chain and the actors involved is essential to implement strategies that maximize the value of Peruvian quinoa at each stage.
Post-pandemic challenges and opportunities
The COVID-19 pandemic shook the global economy, and the quinoa industry in Peru was no exception. However, as with any crisis, both challenges and opportunities emerge. Analyzing the direct and indirect impacts of the pandemic on the quinoa sector, as well as the responses and adaptations of the actors involved, is essential to chart a path towards a solid and sustainable recovery.
Impact of COVID-19 on exports
- Supply chain disruption: Mobility restrictions and quarantine measures affected export logistics, from land transportation to ports and airports, creating delays and increasing costs.
- Market closures: Many countries receiving Peruvian quinoa implemented closures and restrictions that affected demand for the product, especially in the restaurant sector.
- Price Fluctuations: Uncertainty and disruptions in the supply chain led to price fluctuations, impacting both producers and consumers.
- Technological adaptation: Confinement accelerated the adoption of digital technologies for the sale and promotion of quinoa, opening new channels and market strategies.
Recovery and adaptation of the sector
- Supply chain resilience: Companies and cooperatives have sought to strengthen and diversify their supply chains to be more resilient to possible future shocks.
- Adaptation to the digital market: The rise of e-commerce and online sales platforms has opened new opportunities for Peruvian quinoa, reaching consumers who were previously inaccessible.
- Revaluation of the local product: The pandemic has led many consumers to revalue local and sustainable products, and quinoa, with its rich tradition and nutritional benefits, is in a privileged position to satisfy this demand.
- Cooperation and solidarity: Cooperatives, organizations and companies in the sector came together in times of crisis to share resources, knowledge and strategies, strengthening the social and economic fabric of the sector.
The post-pandemic has posed unprecedented challenges for the quinoa sector in Peru, but it has also brought with it new opportunities and learnings that, if properly used, can consolidate and expand the position of Peruvian quinoa in the global market.
Success stories and learnings
The world of Peruvian quinoa is full of inspiring stories and valuable learnings. Knowing those actors who have succeeded in the international market, as well as identifying the keys to their success, can serve as an invaluable guide for new producers and exporters. At the same time, understanding the lessons learned, both from successes and failures, is essential to navigate this dynamic market.
Stories of successful exporters
- Alisur SA: As one of the main players in the export of quinoa, Alisur SA is a clear example of how to identify and take advantage of specific market niches, adapting to the changing needs of consumers.
- Innovation and adaptation: There are companies that, beyond selling quinoa in its traditional format, have known how to diversify their offer with derived products, conquering palates and opening new opportunities.
- Connection with roots: Some producers have stood out for their focus on highlighting the Peruvian tradition and culture associated with quinoa, achieving a unique connection with consumers interested in authenticity and the story behind the product.
- Sustainability as added value: There are exporters who have brought sustainability to the core of their business, certifying their quinoa as organic or implementing responsible agricultural practices, which has opened doors to markets with eco-conscious consumers.
Lessons learned and recommendations
- Knowing the consumer: Understanding the consumer’s preferences, needs and values is essential to adapt the offer and communication effectively.
- Networks and collaborations: Building a solid network with other producers, exporters and stakeholders is key to sharing knowledge, accessing new markets and facing challenges together.
- Adaptability: In such a dynamic market, the ability to quickly adapt to changes, whether technological, logistical or consumer, is a fundamental characteristic.
- Investment in quality: Ensuring product quality from cultivation to final packaging is essential to maintain and grow in the international market.
The success stories in the world of Peruvian quinoa show us that, with passion, dedication and a well-defined strategy, it is possible to conquer the palates of the world and, at the same time, contribute to the sustainable development of Peru.
Conclusion: The future of Peruvian quinoa in the global market
The journey through the history, production, export and potential of Peruvian quinoa in the global market offers a panorama full of opportunities and challenges. Quinoa, being an ancient food with deep roots in the Andean culture, has proven to be not only a superfood in nutritional terms, but also a superproduct in its economic and social potential for Peru.
Recap of key points
- History and value of quinoa: Peruvian quinoa has a legacy that transcends generations, offering the world a complete and versatile food.
- Strategic markets: While the United States has been a pillar in exports, emerging and established markets in Europe and other continents represent significant opportunities.
- Competition and differentiation: Despite the growth of global competitors, Peruvian quinoa has opportunities for differentiation through quality, branding and sustainable practices.
- Socioeconomic impact: The export of quinoa has promoted rural development, job creation and strengthening of local communities.
- Challenges and adaptation: The quinoa value chain faces challenges from production to export logistics, but adaptability and innovation remain keys to success.
Final reflection and call to action
Peruvian quinoa is more than a grain; It is a story of culture, tradition and opportunity. As the world continues to recognize its benefits and versatility, the potential for growth is undeniable. However, to continue to thrive in a competitive global market, it is essential that stakeholders, from farmers to exporters and politicians, collaborate, innovate and maintain an unwavering commitment to quality and sustainability.
The call is to continue strengthening the “Peruvian quinoa” brand, investing in research, development and training, and creating strategic alliances that allow Peru to continue being an undisputed leader in the global quinoa market. The journey will not be without challenges, but with unity, vision and determination, the future of Peruvian quinoa is promising.